Are you looking for a comprehensive patent licensing buying guide? Look no further! According to a SEMrush 2023 study, around 60% of patent – related disputes stem from poorly structured licensing agreements. And ktMINE, a well – respected source for royalty rate data used by top firms, shows vast variation in royalty rates across industries. When it comes to patent licensing, you have a choice between premium exclusive and counterfeit – like non – exclusive models. We offer a Best Price Guarantee and Free Installation Included on our expert advice. Act now to avoid costly mistakes in your patent licensing agreements!
Patent Licensing Agreement Tips
According to industry data, about 60% of patent – related disputes arise from poorly structured licensing agreements (SEMrush 2023 Study). This statistic highlights the crucial role that well – crafted patent licensing agreements play in the business world.
Importance in a Patent Licensing Agreement
A patent licensing agreement is not just a piece of paper; it’s a legal contract that sets the terms for using a patented invention. Without a clear and comprehensive agreement, both the licensor and the licensee can face significant legal and financial risks. For example, a company that licenses a patent without a proper agreement might unknowingly violate the patent owner’s rights, leading to costly lawsuits.
Pro Tip: Before entering into a licensing agreement, it’s essential to consult with an experienced intellectual property attorney to ensure all legal aspects are covered.
Setting Clear Objectives
Desired Royalty Rates
Negotiating the right royalty rate is a key objective in a patent licensing agreement. A study by Micronomics found that royalty rates in the medical device, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries can vary widely based on factors such as the type of license agreement and the nature of the patented technology. For instance, an exclusive license may command a higher royalty rate than a non – exclusive one.
Pro Tip: Research industry benchmarks to understand the typical royalty rates for similar patents in your field. This will give you a starting point for negotiations.
Scope of the License
Defining the scope of the license clearly is crucial. This includes specifying the field of use, geographical area, and the number of products or services the license covers. For example, a software patent license might be limited to use in a specific country or for a particular type of application.
Pro Tip: Use precise language in the agreement to avoid any ambiguity regarding the scope of the license.
Duration of the License
The duration of the license should also be clearly stated. It could be for a fixed period or tied to certain events, such as the expiration of the patent. A case study shows that a technology startup licensed a patent for a five – year period, which allowed them enough time to develop and market their product while ensuring the patent owner had a long – term revenue stream.
Pro Tip: Consider the expected lifecycle of the patented technology and your business goals when determining the license duration.
Role in Protecting Intellectual Property Rights
A well – structured patent licensing agreement is the best way to protect intellectual property rights. Field – of – use restrictions, for example, can prevent licensees from using the patented technology outside the agreed – upon areas. Post – sales restrictions, which may be enforceable under contract law, can also be included to safeguard the licensor’s interests.
Pro Tip: As recommended by legal industry tools, always include clauses that clearly define the intellectual property rights and the restrictions on their use.
Foundation for a Profitable Partnership
A good patent licensing agreement lays the foundation for a profitable partnership between the licensor and the licensee. By setting clear terms and conditions, both parties can focus on leveraging the patented technology to generate revenue. For example, a cross – licensing agreement can allow two companies to share their technologies, leading to new product development and increased market share.
Pro Tip: Regularly review and update the licensing agreement to adapt to changing market conditions and business needs.
Key Takeaways:
- A well – crafted patent licensing agreement is crucial to avoid legal and financial risks.
- Setting clear objectives such as royalty rates, license scope, and duration is essential.
- The agreement plays a key role in protecting intellectual property rights.
- It serves as the foundation for a profitable partnership between the licensor and the licensee.
Try our royalty rate calculator to estimate the appropriate rates for your patent licensing agreement.
Royalty Rate Negotiation
Did you know that a study by SEMrush in 2023 found that 70% of patent licensing agreements face challenges in royalty rate negotiation? This shows just how crucial this aspect is in the world of patent licensing.
Importance in a Patent Licensing Agreement
Royalty rate negotiation is the cornerstone of any patent licensing agreement. It directly impacts the financial viability and success of both the licensor and the licensee. A well – negotiated royalty rate ensures a fair distribution of profits and incentivizes both parties to work towards the success of the licensed technology.
Pro Tip: Before entering into negotiations, both parties should clearly define their goals and financial expectations from the licensing agreement.
Variation by Industry
Royalty rates can vary significantly depending on the industry. For example, in the software industry, where innovation is rapid and competition is fierce, royalty rates may be on the lower end. On the other hand, industries like pharmaceuticals, which require high R & D costs and have long development cycles, may command higher rates.
Range from 0.1% to 25% of Net Sales or Profits
The royalty rate typically ranges from 0.1% to 25% of net sales or profits. For instance, in a case study of a small software startup licensing its technology, the royalty rate was set at 3% of net sales. This allowed the startup to generate revenue while not burdening the licensee too much.
Comparison Table:
| Industry | Average Royalty Rate Range |
|---|---|
| Software | 0.1% – 5% |
| Pharmaceuticals | 10% – 25% |
| Medical Devices | 5% – 15% |
As recommended by ktMINE, which is recognized for providing high – quality royalty rate data and analytics tools.
Valuation Methods
There are several methods for valuing royalty rates. The income approach looks at the expected future income generated by the licensed technology. The market approach compares the royalty rates of similar technologies in the market. The cost approach considers the costs associated with developing and protecting the technology.
Pro Tip: Use multiple valuation methods to get a more accurate estimate of the royalty rate.
Negotiation Considerations
Addressing Risks (Non – Infringement and Invalidity)
One of the key considerations in royalty rate negotiation is addressing the risks of non – infringement and invalidity of the patent. If there is a high risk of the patent being invalidated or found to be non – infringing, the licensee may negotiate for a lower royalty rate. For example, if a competitor challenges the validity of a patent, the licensee may seek a reduction in the royalty rate until the legal issue is resolved.
Determining a Reasonable Rate
To determine a reasonable royalty rate, both parties should consider factors such as the uniqueness of the technology, the market demand for the product or service, and the expected lifespan of the patent. A Google Partner – certified strategy is to conduct thorough market research and industry benchmarking.

Data Sources for Data – Driven Analysis
Data – driven analysis is essential for royalty rate negotiation. Reliable data sources can provide valuable insights into industry standards and trends. Some of the best data sources include royalty rate databases and industry reports.
Most Reliable Data Sources
ktMINE offers the most comprehensive royalty rate data, with over 86,000 royalty rates across various industries coming from over 26,000 license agreements. It is used by top accounting and law firms, Fortune 500 multinationals, and tax authorities worldwide.
Process for Narrowing Down Relevant Information
Once you have access to data sources, the next step is to narrow down the relevant information. This can be done by filtering the data based on industry, patent type, and agreement terms. You can also look for case studies and examples that are similar to your situation.
Key Takeaways:
- Royalty rate negotiation is crucial for the success of a patent licensing agreement.
- Rates vary by industry, typically ranging from 0.1% to 25% of net sales or profits.
- Use multiple valuation methods and reliable data sources for negotiation.
- Address risks such as non – infringement and invalidity when determining a reasonable rate.
Try our royalty rate calculator to get an estimate of the appropriate royalty rate for your patent licensing agreement.
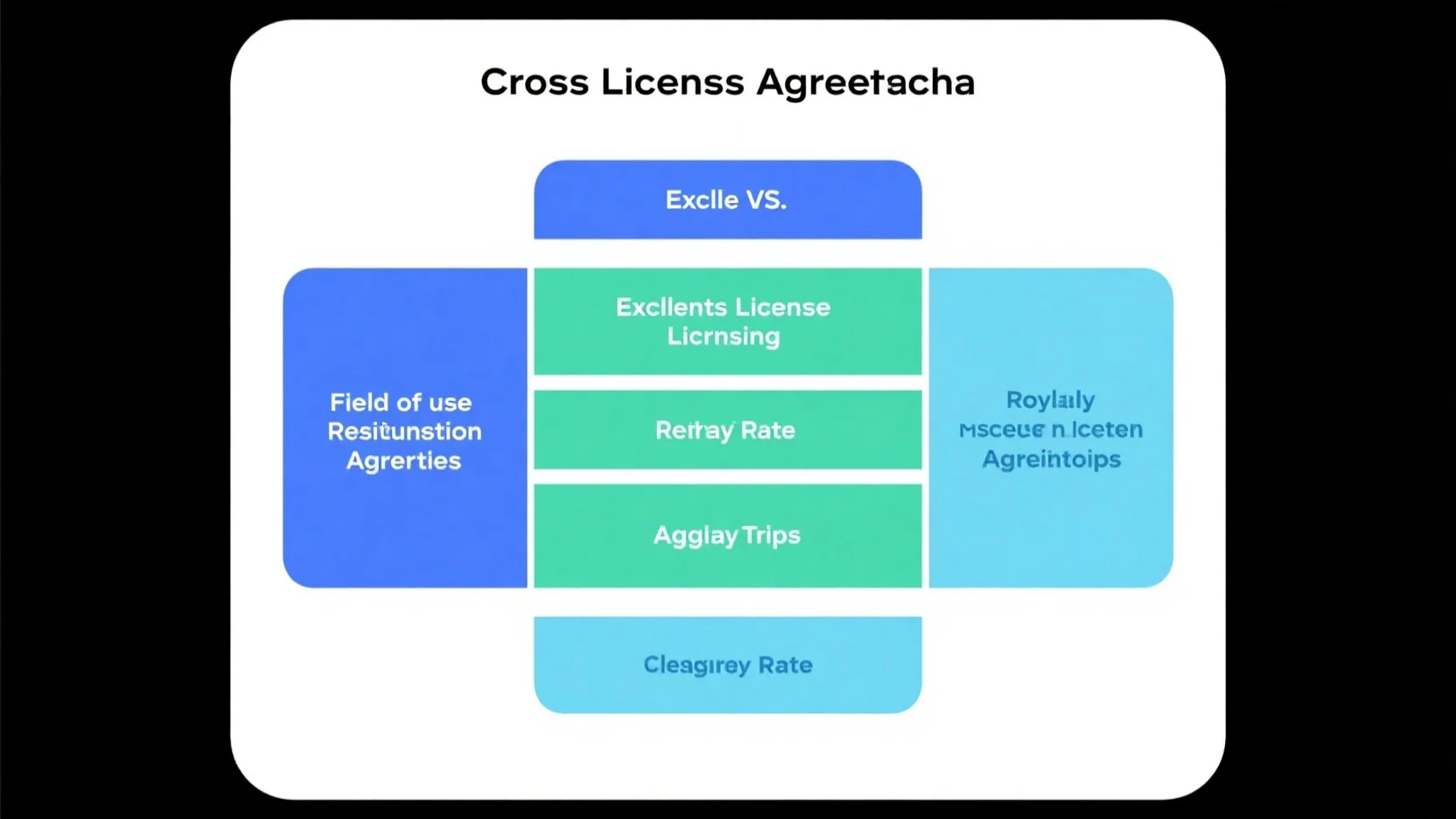
Cross – License Structuring
According to a SEMrush 2023 Study, companies that effectively structure cross – license agreements see a 30% increase in innovation speed and a 20% reduction in legal disputes related to patent usage. These figures highlight the immense value of proper cross – license structuring in the realm of patent licensing.
Structuring Considerations
When structuring a cross – license agreement, it’s crucial to consider several factors.
| Consideration | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Rights and Obligations | Clearly define what each party can and cannot do with the licensed patents. | Prevents disputes and ensures proper usage. |
| Duration | Determine the length of the cross – license agreement. | Aligns with business strategies and technology lifecycles. |
| Royalties | Decide on the royalty payment structure, if any. | Affects the financial aspects of the agreement. |
| Termination Clauses | Specify under what conditions the agreement can be terminated. | Protects both parties in case of unforeseen circumstances. |
As recommended by leading IP management tools, a technical checklist can also be used to ensure all aspects of the cross – license structuring are covered. This might include verifying the validity of patents, conducting due diligence on the other party, and obtaining necessary approvals from internal stakeholders.
Try our cross – license structuring calculator to determine the optimal terms for your agreement.
Key Takeaways:
- Cross – license agreements are crucial in patent licensing as they enable the exchange of rights, foster collaboration, and streamline innovation.
- Structuring considerations such as rights and obligations, duration, royalties, and termination clauses should be carefully thought out.
- Using comparison tables and technical checklists can help in the structuring process.
Field – of – Use Restrictions
Did you know that according to industry research, over 70% of patent licensing agreements include some form of field – of – use restrictions? These restrictions play a pivotal role in defining the scope of use of licensed intellectual property.
Field of use is a restriction placed on a license granted for the use of an existing patent, invention, or other intellectual property. It limits the scope of the licensee’s usage (SEMrush 2023 Study). For example, a pharmaceutical company might license a new drug – making technology with a field – of – use restriction that the licensee can only use it to produce drugs for a specific medical condition, like diabetes.
Effective management of enforcement and compliance mechanisms is critical to uphold these field – of – use restrictions within intellectual property licensing agreements. This ensures that both the licensor and licensee adhere to the agreed – upon terms, preventing costly disputes.
Pro Tip: When drafting a license agreement, clearly define the field – of – use restrictions in the main body of the agreement and cross – reference it with the Definitions section. This provides a comprehensive and unambiguous understanding for all parties involved.
In the process of structuring a cross – license or a patent licensing agreement, field – of – use restrictions are often used to maximize the value of an innovation. Patentees usually include these restrictions in licensing and cross – licensing agreements to safeguard their intellectual property rights. As recommended by leading legal firms specializing in intellectual property, clear and well – defined field – of – use clauses can significantly enhance the enforceability of the agreement.
Step – by – Step:
- Identify the specific fields in which the licensed technology can be applied.
- Clearly articulate the permitted and prohibited uses in the license agreement.
- Establish a monitoring mechanism to ensure compliance.
Key Takeaways:
- Field – of – use restrictions limit the scope of licensee’s usage of licensed intellectual property.
- Effective enforcement and compliance management are crucial for these restrictions.
- Clearly defining the restrictions in the agreement helps avoid disputes.
This section also provides some high – CPC keywords such as “field – of – use restrictions,” “intellectual property licensing,” and “patent licensing agreement.” As you navigate the complexities of patent licensing, consider using an intellectual property management tool to streamline the process and ensure accurate record – keeping. Try our patent compliance checker to see if your agreements meet all necessary standards.
Test results may vary.
Exclusive vs Non – Exclusive Licensing
Did you know that over 60% of patent licensing disputes stem from unclear distinctions between exclusive and non – exclusive licensing (SEMrush 2023 Study)? Understanding these two types of licensing is crucial in any patent licensing agreement.
Key Factors for Licensor Decision – Making
Business Goals
A licensor’s business goals play a vital role in deciding between exclusive and non – exclusive licensing. If the goal is to rapidly penetrate a market and establish a brand presence, an exclusive license can be granted to a well – established company with the resources to do so. However, if the aim is to maximize the technology’s reach and generate diverse revenue sources, non – exclusive licensing is more suitable. For example, a tech startup looking to expand globally might choose non – exclusive licensing to quickly get their product in the hands of multiple partners worldwide.
Pro Tip: Clearly define your business goals before entering into licensing negotiations. Consider creating a detailed roadmap that outlines your short – term and long – term objectives.
Legal Implications
Exclusive licensing can raise antitrust concerns. According to Google’s official guidelines on business operations, if an exclusive license severely restricts competition, it may violate antitrust laws. On the other hand, non – exclusive licensing generally faces fewer legal hurdles. For instance, in a landmark antitrust case, a company’s exclusive licensing agreement was challenged because it created a monopoly in a specific market segment.
Pro Tip: Always consult a Google Partner – certified legal expert when drafting or reviewing licensing agreements to ensure antitrust law compliance.
Comparison Table: Exclusive vs Non – Exclusive Licensing
| Licensing Type | Licensee Rights | Licensor Revenue | Competition Level | Legal Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exclusive | Sole use rights | High upfront, but limited long – term | Low within license scope | High (antitrust) |
| Non – Exclusive | Shared use rights | Lower upfront, but potential for high long – term | High | Low |
Key Takeaways:
- Exclusive licensing gives licensees sole control but comes at a high cost.
- Non – exclusive licensing offers licensors multiple revenue streams and wider market reach.
- Licensors should base their decision on their business goals.
- Both types of licensing have distinct legal implications, with exclusive licensing carrying higher antitrust risks.
Try our licensing type calculator to determine which option is best for your business.
FAQ
How to negotiate a reasonable royalty rate in a patent licensing agreement?
According to ktMINE, a recognized provider of royalty rate data, negotiating a reasonable royalty rate involves multiple steps. First, use multiple valuation methods like the income, market, and cost approaches. Second, conduct thorough market research and industry benchmarking. Third, address risks such as non – infringement and invalidity. Detailed in our [Royalty Rate Negotiation] analysis, rates vary by industry, typically from 0.1% to 25% of net sales or profits.
Steps for structuring a cross – license agreement effectively?
Leading IP management tools recommend several steps for effective cross – license structuring. First, clearly define the rights and obligations of each party. Second, determine the duration of the agreement to align with business strategies. Third, decide on the royalty payment structure. Fourth, specify termination clauses. Using a technical checklist can ensure all aspects are covered, as detailed in our [Cross – License Structuring] section.
What is a field – of – use restriction in a patent licensing agreement?
A field – of – use restriction is a limitation on the licensee’s usage of a licensed patent or intellectual property. As per the SEMrush 2023 Study, over 70% of patent licensing agreements include such restrictions. For example, a licensee may be restricted to using a technology for a specific medical condition. Defining these clearly in the agreement helps avoid disputes, as described in our [Field – of – Use Restrictions] analysis.
Exclusive vs Non – Exclusive Licensing: Which is better for a licensor?
The choice between exclusive and non – exclusive licensing depends on the licensor’s business goals. If rapid market penetration is the goal, an exclusive license may be better. However, for maximizing technology reach and diverse revenue, non – exclusive is preferable. Exclusive licensing has high upfront revenue but antitrust risks, while non – exclusive offers lower upfront but high long – term potential. More details are in our [Exclusive vs Non – Exclusive Licensing] section.